FAQ
Consultation of Autologous Cancer Vaccine and Consultation Methods
1. I would like a detailed consultation, what should I do?
The best way is to contact us through a partner clinic. Contact us her.
2. How can I get medical treatment?
(1) Make an appointment for medical treatment with a partner hospital or clinic by telephone or email. At this time, ask the physician currently in charge and secure the cancer tissue (surgical formulation or cancer tissue stored in paraffin) when undergoing surgery. Cancer tissue having a volume of 1.5 g or more, if possible 2 g (as a guideline, 2 cm x 1 cm x 1 cm square or more, about the size of a 2-Euro coin with a thickness of 2 mm) is required. In the case of paraffin-stored blocks, secure as much cancer tissue as possible (preferably 3 to 4). For this reason, the cooperation of your physician is essential.
(2) Accept the first visit at the place of reservation. At this time, you will be given an explanation of the autologous cancer vaccine treatment and a consent form.
Cancer Immunotherapy and Autologous Cancer Vaccine Therapy
3. What is an autologous cancer vaccine?
In the raw material, since the patient’s own cancer tissue is treated with formalin and chemically fixed, all cancer cells are killed off and the formalin is eliminated by washing. An immune stimulant (adjuvant) is mixed with the finely crushed and fixed fragments of cancer tissue and suspended in a physiological saline solution for injection as the autologous cancer vaccine. Adjuvant is a generic term for a group of substances that strongly stimulates immune cells whereby the stimulated cells release active ingredients (cytokines) that in turn stimulate other types of immune cells. This creates a chain reaction. From among the many types of adjuvants, we use a safe agent like tuberculin, widely used in Japan, for autologous cancer vaccines.
4. What are the characteristics of cancer immunotherapy compared with other cancer treatment methods
Traditional cancer treatment methods include surgery, radiation therapy and anticancer drug therapy. In principle, surgery is the first choice and in principle the cancer is excised. However, if surgery cannot be performed or if metastasis or a relapse has occurred, radiation therapy and anticancer drug therapy will be performed instead.
On the other hand, cancer immunotherapy is designed to strengthen the immunity in the body programmed since birth to eliminate cancer cells. In some cases, the immune system mainly attacks the foreign matter by making antibodies and the body’s immune cells such as lymphocytes then attack the foreign matter directly. Autologous cancer vaccine therapy is a type of cancer immunotherapy and is characterized by its few side effects.
5. What is the difference between autologous cancer vaccine therapy and a therapy using natural killer cells
Autologous cancer vaccine therapy is employed to induce and propagate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) that kill only autologous cancer cells in the body. The specificity of CTL is very high as it kills only particular cancer cells. Even when there are cancers of a different type, these are not killed. If cancer antigen (TAA) is different at all, it is in that it cannot recognize other cells as an enemy. Instead it is recognized as an enemy, the killing potential against such cells (e.g. cancel cells, foreign substances) is very high.
In contrast, natural killer cells (NK) kill cancer cells even when there are no abnormal markers.
Unless cancer cells resist, the role sharing differs between CTL and NK.
6. What is the difference between autologous cancer vaccine therapy and immune cell therapy performed in other clinics?
See the following table. For the difference from natural killer cell therapy, see 5 and 13 .
Difference between autologous cancer vaccine therapy and general immune cell therapy
| Autologous Cancer Vaccine Therapy | General Immune Cell Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Materials | Patients with their own cancer tissue 1.5 grams or more excised by sur-gery and preserved in formalin (or hardened with paraffin). Formalin is washed away to below the detection limit. | The patient's own blood, 15 ml or more. Depend- ing on the method, several liters may be circulated blood. |
| Length of Treatment | 5 days after receipt of cancer tissue | After taking blood, usually over two weeks. In the case of dendritic cell therapy around 10 days. |
| Stability | Because it does not contain living cells, it is stable for several months in a refrigerator | Because living cells are used immediately after the end of incubation (stable if stored for several months if cryopreser-vation is possible, but re-culture is then required) |
| Dosage | As a general rule, it ends three times in total, once every other week (a total of 5 times even including pre- and post- immunization reaction tests) | It is common to repeat this for several courses or more, once biweekly performed 5-6 times as one course |
| Immune cells that attack cancer? | It will be activated in the body | It is cultivated outside the body to activate, but due to complications, there are many cases where you are administering it without confirming the efficacy |
| Specificity | Highly specific. Will attack only the targeted cancer | [In the case of activated lymphocytes] The specificity is low, if any cancer is administered expecting to attack dendritic cells case specific. Depending on the type of cancer antigen given at the same time |
| Efficacy | When immune cells are activated in the body, it acts very strongly on the targeted cancer cells and attacks it, and it does not affect any other normal cells at all | Efficacy is relatively weak. Therefore, repeated administration is probably required |
| Type of Cancer | In principle any kind can be used | In principle any kind can be used |
| Type of Cancer | In principle any kind can be used | In principle any kind can be used |
| Side Effects | None to worry about | None to worry about |
| Hospitalization | Not required. Can be done on outpatient basis | Not required. Can be done on outpatient basis |
| Cost | About EUR 16,700 in total | In dendritic cell therapy, approx EUR 17,000 to 26,000 depending on the type of cancer antigen and the number of administrations |
Principle of autologous cancer vaccine
7. Explain the principle of autologous cancer vaccine action. Why is it effective?
Killer cells (part of lymphocytes) that kill and eliminate normal cells are inherent in the human body when normal cells become abnormal due to a reason. Killer cells are mainly cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer cells (NK). However, because cancer cells are very similar to normal cells, killer cells are usually not activated to kill cancer cells quickly.
Cancer vaccine therapy is a therapy that activates killer cells by stimulation and inducing them to kill cancer cells in the body. In autologous cancer vaccine, we use formalin-treated cancer tissue of the patient as a stimulant (including dead cancer cells). This acts to increase lymphocytes in the body and activates and spreads killer cell popula-tions. Killer cells usually play a role in killing virus-infected cells and injured cells and removing them from the body. A part of its important role is to kill cancer cells.
8. Why are killer cells activated when inoculated with autologous cancer vaccine? Provide more details.
The cancer antigen (TAA) contained in the formalin-treated and chemically fixed cancer tissue becomes an “abnormal marker” and is responsible for the killer cell-stimulating action.
When inoculated with autologous cancer vaccine, the dead cancer tissue will be taken up by cells that present antigens such as dendritic cells (DC) and digested by it. A part of the digested TAA is presented to the helper T cell, and the helper T cell is activated, which stimulates the killer T cell. This killer T cell is CTL which recognizes TAA appearing on the surface of living cancer cells and kills the cancer cells. T lymphocytes underlying CTL are everyone, flowing through the blood. However, it is necessary to recognize TAA, train and spread the killer cells. The role of the trainer is the dendritic cell. Dendritic cells take up and kill the dead cancer cells and transmit the information to helper T cells. Helper T cells are activated to release another kind of cytokines which activate and spread T lymphocytes underlying CTL. It is also known that dendritic cells directly contact and activate CTL at this time.
Efficacy and treatment outcome of autologous cancer vaccine
9. Is there a solid scientific basis for the clinical effect?
Yes. Experts please refer to the paper published in the official academic journal of the American Cancer Society (Clinical Cancer Research, 10: 1574-1579, 2004). In liver cancer cured by surgery, the post-surgery recurrence rate is very high so the prognosis is usually negative, due to the absence of effective recurrence prevention. Such a group of patients was randomly divided into two groups, and showed the recurrence prevention effect after autologous cancer vaccine was administered to one group. See “The effect of suppressing recurrence of liver cancer by autologous cancer vaccine – 1”.
Among them, the red line shows the subsequent course of the autologous cancer vaccine administration group (18 cases). Compared to the progress of the 21 cases in the control group (blue line, group not receiving autologous cancer vaccine) who underwent hepatocarcinoma operation during the same operation, this shows a clear difference in statistical significance (Log-rank test, P = 0.003).
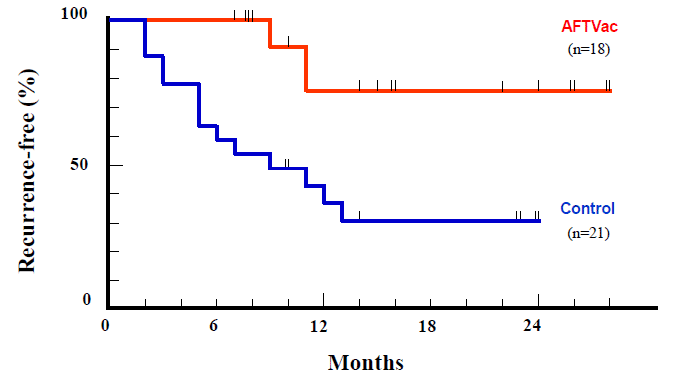
Recurrence-free survival
Even if surgically curable, it can be seen that in the control group not receiving autologous cancer vaccine treatment, recurrence is more frequent and the number of relapsed cases without disease rapidly declines. It is not a technical problem of surgery, it shows the rate of liver cancer occurring as a result of cirrhosis.
In addition, the illustration “Inhibition of Recurrence of Liver Cancer By Autologous Cancer Vaccine – 2” shows the prognosis of life of vaccine administration group and control group.
With autologous cancer vaccine therapy, a clear survival benefit is observed in postoperative liver cancer (log-rank test, P = 0.01). In other words, when receiving autologous cancer vaccine therapy after liver cancer surgery, the rate of survival is clearly increased by suppressing the recurrence of liver cancer. Also refer to the part of A34 showing examples other than liver cancer.
In addition, in brain tumors (grade IV glioblastoma, said to be the worst of all), cases in which clear residual tumor reduction and disappearance are observed after autologous cancer vaccine administration (see the part surrounded by the yellow line), partial shrinking example, cases without increasing and becoming a variant have been observed, with a response rate of 17% and disease control rate of 45%. Interested readers may refer to the paper published in the official academic journal of the Cancer Society of Japan (Cancer Sci., 98 (8): 1226-1233, 2007).
In this case, the median overall survival from the first surgery is 24 months while the presentation data when the anticancer agent Temodar (approved for brain tumor treatment) is used (median overall survival 14.6 months, N Engl J Med 352: 987-996, 2005).

Overall survival

Besides, there are also cases in which blood tumor markers continued to decline for almost a year during periods when only “self-cancer cancer vaccine” therapy was performed with lung cancer, or conventional common sense when used in combination with a weak anti-cancer drug. There are also cases of breast cancer in which bone metastasis was drastically reduced unexpectedly. In combination with radiotherapy, there are cases of breast cancer patients who survived after palliative care wards and were discharged or cases where metastatic lesions of giant lymph nodes not responding to anticancer drugs disappeared.
10. Are autologous cancer vaccines effective for cancers other than “liver cancer” and “brain tumor” that have obtained results in clinical studies?
Yes. Autologous cancer vaccine is a Phase I / Phase II early clinical trial demonstrating the effect of suppressing recurrence of liver cancer · prolongation of overall survival (Clinical Research, 10: 1574-1579, 2004). Even in cancers other than liver cancer, the way to make the vaccine is exactly the same, and since we use the patient’s own cancer tissue as raw material, the abnormal marker (TAA, cancer antigen) lurking in it is recognized. If the vaccine succeeds in activating killer lymphocytes in the body, it is considered to be effective as well.
11. What kind of cancer is it effective against?
If autologous cancer vaccine can activate killer cells aimed at cancer cells in the patient’s body, it can be expected to be effective regardless of the kind of cancer that is targeted. However, if the proliferation speed of cancer cells is faster than the proliferation speed of CTL, CTL proliferation cannot catch up, so cancer cells cannot be killed completely. Therefore, in patients who have progressed too much and at the end of the term, “self-cancer vaccine therapy” may not be possible. In addition, cancer cells may have troublesome variations that do not indicate their abnormal markers (TAAs). In that case, CTL cannot be recognized as an enemy and will be missed. As a result, recurrence and metastasis occur rather than the elimination of the cancer. This probability will rise with the degree of cancer terminality.
However, among the killer cells, NK will kill any abnormal cell that is not in the body, if there is no such marker. However, it cannot be killed if the inhibitory molecule that prevents the other cell from being killed by NK (which is also one of the molecules indicating the mark to CTL). Normal cells have this inhibitory molecule, and the markers shown are normal. Cancer cells often do not have this inhibitory molecule, but in rare cases there are cases.
Therefore, if a cancer cell has a molecule showing an abnormality marker, CTL will kill and if it does not have a molecule showing abnormal marker (in the absence of an inhibitor molecule) NK can kill. There are, however, a few cases in which by coincidence cancer cells have inhibitory molecules that do not have molecules indicating abnormal markers and are not killed by NK. In this unlikely event, cancer immunotherapy does not work.
12. How long will the effect of autologous cancer vaccine last?
For cancer cells expressing abnormal markers (TAA, cancer antigens) described on A8 which are exactly the same as the molecules for cancer cells expressing on the cell surface, after mass proliferation of killer T cells capable of killing them, memory T cells As long as its memory T cells are alive, repeatedly stimulating killer T cells to activate and proliferate, the effect is considered to be protracted.
13. Do you study “self-cancer cancer vaccine” therapy by Cell Medicine Co. Ltd. at university hospitals?
Yes. Starting from July 2002, a pilot study began at the University of Tsukuba · Neurosurgery, about clinical research of “self-cancer cancer vaccine therapy”, Kanazawa University, Gastroenterology Department. At the Tokyo Women’s Medical University · Neurosurgery Department, collaborative research has also been conducted with Cell Medicine Co., Ltd. with approval from the Ethics Committee.
Specific treatment of autologous cancer vaccines
14. How is the dosing schedule?
The treatment of autologous cancer vaccine therapy progresses by injection at outpatient clinic. The dosing schedule advances as shown in the figure and injections are made with three vaccines at an immunoeefficacy test. Immunological response tests are performed to examine the presence of immunological reactions in the body but as there is no treatment effect, these may be omitted. Basically, the autologous cancer vaccine is administered three times at intervals of 2 weeks but the administration interval may be changed depending on cancer type and the patient.
15. If I get positive in the first immunological reaction test, is there no effect if I receive a cancer vaccine?
It is rare that the first DTH-1 reaction test is positive. (Positive results suggest that killer T cells are found and cancer cell are already being eliminated in the body done. However, a confirmation that there are no unexpected hypersensitivity reactions is still needed.
However, in rare cases there are those who become positive in the first DTH-1 reaction test. For example, in patients with oral cancer, oral bacteria have penetrated into the cancer tissue, so the first immunological reaction test can be positive. However, this is an immune response to oral bacteria, not an immune response to oral cancer. In addition, what also may happen is that despite the first DTH-1 reaction test being negative, erythema appeared at the injection site of the DTH-1 response test after vaccination, and did not wait for the second DTH-2 reaction test. This suggests that strong cellular immunity was induced in the body as soon as possible against the fixed cancer tissue still remaining at the injection site of the first DTH-1 reaction test. This is never an abnormal phenomenon so there is need for concern.
16. Is it possible to receive autologous cancer vaccine therapy without cancer surgery?
Not really. Even if no cancer surgery is undertaken, this is possible only when the patient’s own cancer tissue previously removed by surgical operation is provided (formalin-treated tissue or paraffin-embedded block). The patient in the following figure had breast cancer, but it was possible to administer the autologous cancer vaccine because the paraffin-embedded block of the breast cancer tissue surgically excised more than a year earlier remained intact.
However, if you have never undergone surgery, there is no cancer tissue to be used as a raw material so unfortunately a self-cancer vaccine cannot be produced. Even though it is not a major surgery if it is easy to extract cancer tissue of 1.5 g or more with an endoscope, a thoracoscope, a laparoscope or similar. An autologous cancer vaccine can be made from the cancer tissue. Please consult your physician.
17. Is hospitalization required?
No, autologous cancer vaccine therapy can be completed on an outpatient basis.
18. Can I receive autologous cancer vaccine therapy in combination with other cancer treatments I currently receive? What are the points to be noted in that case?
If other cancer treatment methods do not inhibit the body’s immune reaction, such as using a steroid drug or using a strong intrinsic anticancer drug that causes bone marrow suppression, an autologous cancer vaccine therapy (Please note that intense anti-cancer drugs, which are standard treatment for surgery and inoperable cases, have a strong immunosuppressive effect, especially lymphocyte proliferation inhibiting efficacy). In the case of radiation therapy, if it is known beforehand that radiation irradiates only the local region of the cancer tissue and does not damage the bone marrow / lymph node that is the manufacturer of the immune cell, at the same time, “autologous cancer vaccine “Therapy may be used in combination.
Anticancer drugs can also be used in combination as long as they have weak immunosuppressive effects. Combination studies are being conducted overseas, and if you pay enough attention to maintaining the number of lymphocytes, it is said that it is rather better to use it in combination. However, in terms of which cancer and what degree of anticancer drug can be used in combination with each other, the low dose used for so-called “diapause therapy” and the time difference combination instead of (simultaneous combination) will be a measure of some degree. Please contact the physician in charge of the hospital.
19. I am currently receiving treatment at another hospital. How can I get autologous cancer vaccine therapy?
Please consult with your physician who is receiving treatment frankly. If the physician has a deep understanding of cancer immunotherapy, he should be able to fully understand the latest cancer immunotherapy. In that case, we will send “instructions for physician” to patients, so please contact us (please see back cover for contact information). If you are a physician who does not have much understanding of cancer immunotherapy, please request a second opinion at a medical institution affiliated with our clinic.
20. How much does the treatment cost?
Per patient, it will be around EUR 16,700 including initial examination, 1 course (3 times) vaccine administration and two immuno response tests. The autologous cancer vaccine itself will be the same at any affiliated hospital / clinic, but there are differences in the accompanying examinations. For details, contact to the affiliated hospital or clinic directly.
Anticancer drug treatment seems to be inexpensive, but depending on the type of anticancer drug, if it becomes continuous administration for 2 years, it runs into several EUR 10.000, even with health insurance it may be rather expensive. Given that there are many cases where there are strong side effects, autologous cancer vaccine therapy without problem side effects is relatively inexpensive.
Because the autologous cancer vaccine is hand-made individually for each patient, and it becomes a vaccine exclusively for that patient, such as “home”, because gold teeth are used for dental treatment As in case of inserting) Because it becomes free medical examination and insurance cannot be used, please understand that it will become the price of this degree.
The cost of regular examination at the original hospital or clinic where surgery was undergone will be normal insurance treatment so health insurance can be used, but the costs may differ. Also, at our affiliated hospital /clinic, expenses for needed blood tests and diagnostic imaging as necessary also differ. In this case, as part of free medical examination and insurance cannot be used, please confirm with each hospital / clinic.
Side effects of autologous cancer vaccine
21. Are there any side effects?
To date, autologous cancer vaccine has already been administered to more than 1,800 patients, but severe side effects that become a problem have not been found. However, administration of autologous cancer vaccines to patients who are suspected of having an autoimmune disease is contraindicated because there is a possibility of exacerbation due to a strong immunostimulatory effect.
2 weeks later after vac.
4 weeks later after vac.
Professional Questions
22. Why is an immune reaction, not taking place at the time when a cancer is formed in the body, established when the cancer tissue is returned to the body as a vaccine?
- The key points are injection with adjuvant so that fragments of autologous cancer tissue are directly incorporated into dendritic cells in the body. This high uptake capacity of immature dendritic cells in the body is taken advantage of. Upon ingestion, it transfers to the regional lymph node, where it matures, stimulates helper T lymphocytes, and further activates killer T lymphocytes (especially CTL) through it. When it moves in the body with blood flow, when it comes into contact with cancer cells, it further activates and kills cancer cells while proliferating. If cancer cells are killed, it can be interpreted that cellular immunity has been established. In the state of nature cancer cells are energetic so fragments do not arise from cancer tissues and rarely are taken directly into dendritic cells in the body.
- In order to establish cell-mediated immunity, it is necessary for the cancer cell side to contain cancer antigen, at least to some extent. Although this amount is small, it is completely unknown how much it is necessary in practice. In the case of postoperative liver cancer, autologous liver cancer vaccine clearly has the effect of suppressing the recurrence of liver cancer if it is from 1 gram or more of formalin-fixed cancer tissue (Peng BG, et al. , Jpn JCancer Res 93: 363-8, 2002). Based on our experience, other types of cancer patients saw some margins 1. More than 5 grams are needed. However, this may differs greatly depending on the type of cancer and the individual situation.
- Another important thing is that if MHC-class I molecule is expressed on the surface of cancer cells remaining in the body and no cancer antigen peptide is presented on it, CTL cannot be recognized as abnormal cells That is the point. Expression of MHC-class I is usually said to be infrequent, and one way to stimulate this is IFN-? administration. Some researchers have produced IFN – ? in the body using bacterial components such as BCG – CWS instead of IFN – ? administration. Depending on the type of cancer cell, IFN-? administration may cause MHC-class I expression to be elevated (not necessarily in all cases) and is likely to be killed by CTL.
23. Do you use other people’s materials such as plasma and serum?
We do not use plasma or serum as it is. However, a small amount of human serum albumin is contained in autologous cancer vaccine as a kind of stabilizer. This human serum albumin is a medical drug that is heat-treated so that possibly latent viruses are eliminated without risk.
24. For example, if you have metastasis at two 2 locations with gastric cancer, do you need to make a vaccine from a mixture of cancer tissue. Do you need 1.5 grams or more of each of the two cancer tissues?
No, if the cancer is originally the same, if both the cancer body itself is 1.5 grams or more, you can make a vaccine.
25. Histologically, various organs are made up of a wide variety of cells. In such a structure, it seems that cancer antigens are diverse, and is it impossible to obtain a wide variety of cancer antigens sufficiently quantitatively from 1.5 grams of one cancer tissue?
Yes, that possibility cannot be ruled out. However, the amount of cancer antigen protein in cancer cells is very small. It is too small to measure. Since almost all malignant cancer cells are composed of the same protein as normal cells, only a very small amount of cancer antigen peptides is present the cell surface. Nevertheless, if properly activated immune mechanism, you can discriminate a very small amount of cancer antigen peptides presented on cancer cell surface. So, even if normal tissues are mixed, this does not become a big problem. You only have the minimum amount of cancer antigen that can stimulate the immune system. However, as it is assumed that this minimum amount varies widely among individuals, it is currently the case that efficacy can only be determined by clinical results after autologous cancer vaccine administration.
26. Do you think that all tumor cells are always expressing cancer antigens? If cancer of a type not expressing a cancer antigen exists, it seems impossible to have autologous cancer vaccine therapy?
There are cancer types that do not express cancer antigens. A method of examining whether or not a cancer cell in a patient’s body is expressing a cancer antigen (although it may be possible if there a cancer antigen has already been identified), in the case of targeting against antigens, has not yet been developed.
Nevertheless our autologous cancer vaccine is characterized by its ability to activate immune cells with an unspecified number of unidentified cancer antigens as clues. The choice as to which cancer antigen to use is left to the immune mechanism in the body. As this happens within the body of the same individual, even a very small difference between normal cells and cancer cells can be distinguished. Like a synthetic vaccine, it is not a method of artificially adding antigens from outside the body (the result although desirable may be disappointing).
For that reason, the drug is customized to the individual patient and cannot be used by others.
27. Many anticancer agents cause immunosuppression. Is it possible to combine anticancer drug therapy with autologous cancer vaccine therapy?
In principle, it is possible to use it in combination as long as it is an anticancer drug that does not intensively inhibit lymphocyte proliferation. Also, there is a possibility that self cancer vaccine therapy is administered during the drug withdrawal period of anticancer drug administration or low dosage of anticancer drug is administered. If possible, wait for 4 weeks from entering the drug-free holiday until the effect of anticancer drug disappears, confirm that the number of lymphocytes in the blood is on the way to recovery, and there is still 6 weeks left for autologous cancer vaccine administration. Following this schedule is desirable. If a patient has had a lymphocyte deficiency even once, it must be confirmed that there is a definite recovery. For an example of a case where recovery took a long time, see this paper (? S u YB, et al., JC lin Oncol 22: 610-6, 2004).
However, even in the case where an anticancer drug of relatively weak myelosuppressive effect is administered in a smaller amount than usual, even in the course of administration of FOLFOX or FOLFIRI, the number of blood lymphocytes can be maintained at a constant number or more. When this is the case, simultaneous use is possible. In addition, what has recently appeared and is referred to as molecular targeted drugs or antibody drugs, can be used in combination if it does not inhibit T cell proliferation. As this field is steadily progressing, the conventional thinking about combination use is changing drastically.
28. Are there any worries about immune tolerance and conversely about autoimmune diseases?
I have not seen any of this in the over 1800 cases so far administered. However, because the cancer antigen is unidentified, it is not a strict investigation, and there is no clinical problem which is thought to be due to immune tolerance. On the contrary, it does not cause symptoms similar to autoimmune diseases. The immune system in the body seems to exert extremely severe discriminatory power.
29. I heard that “cancer” is different in nature depending on where it originally occurred. In my case, “cancer” originally occurred in the adrenal gland and spread to the lungs. Is there any effect in such cases?
Autologous cancer vaccine is a Phase I / Phase II early clinical trial demonstrating the effect of suppressing recurrence of liver cancer · prolongation of overall survival time (Clinical Cancer Research, 10: 1574-1579, 2004). Even in cancer other than liver cancer, the way of making the vaccine is the same and uses the patient’s own cancer tissue as raw material, so it can recognize the abnormal marker (TAA, cancer antigen) lurking in it If the vaccine succeeds in activating killer lymphocytes in the body, it will probably be equally effective no matter to where the cancer subsequently spread.














