Frequently Asked Questions About Second-Generation GcMAF
General
Resurrection Clinics Europe is a medical organization in Europe with the purpose of treating patients and developing and producing therapies, in particular immunotherapies such as GcMAF. We work with other clinics and physicians both worldwide as well as with various universities conducting clinical trials and doing research and development.
What is GcMAF?
GcMAF (or Gc Protein-derived Macrophage Activating Factor) occurs naturally in the human body and instructs macrophages to destroy cancer cells and foreign invaders by activating them.
What are macrophages?
Macrophages (Greek for “big eaters”) are cells originating from monocytes, a type of white blood cell found in the body. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense (innate immunity) as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) of vertebrate animals.
Their role is to phagocytize (i.e. engulf and then digest) cellular debris and pathogens, either as stationary or as mobile cells. They also stimulate lymphocytes and other immune cells to respond to pathogens. They are specialized phagocytic cells that attack foreign substances, infectious microbes and cancer cells through destruction and ingestion.
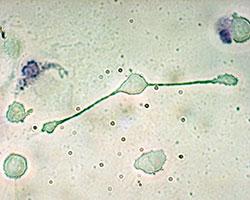 A macrophage of a mouse stretching its “arms” (pseudopodia) to engulf two particles, possibly pathogens.
A macrophage of a mouse stretching its “arms” (pseudopodia) to engulf two particles, possibly pathogens.
Where are macrophages found in the body?
Macrophages and other phagocytes are found in the following locations in the
| Main Location | Types of Phagocytes |
|---|---|
| Skin * | Macrophages, resident Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, mast cells |
| Gut and intestinal Peyer's patches * | Macrophages |
| Lungs * | Macrophages, monocytes, mast cells, dendritic cells |
| Blood | Neutrophils, monocytes |
| Bone marrow | Macrophages, monocytes, sinusoidal cells, lining cells |
| Connective tissue | Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, histiocytes |
| Lymphoid tissue | Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells |
| Spleen | Macrophages, monocytes, sinusoidal cells |
| Thymus | Macrophages, monocytes |
Click edit button to change this text.How does GcMAF work?
GcMAF is a glycoprotein that activates macrophages which in turn increases macrophage effectiveness and transforms them into Natural Killer (NK) cells.
How is GcMAF produced in the body?
Phagocytic activity data show that GcMAF produced from all subtypes are highly effective:
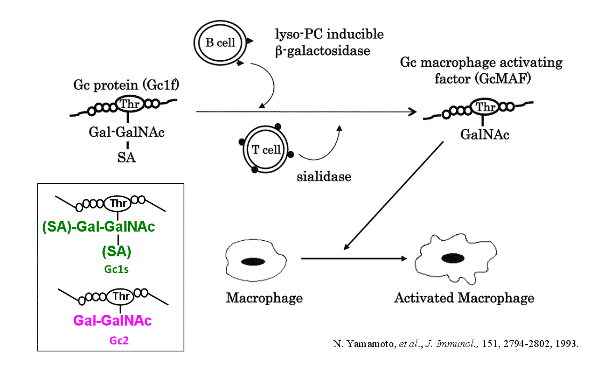
Proposed scheme: Conversion of Gc1f Protein to GcMAF
What is Nagalase?
Classic Nagalase Theories and New Facts
- Alpha-nagalase is an enzyme secreted by cancer cells, virus-infected cells and normal cells
- Two types: Exo-type and endo-type Nagalase
- Nagalase has been reported to accumulate in the blood of cancer patients
- Nagalase deglycosylates vitamin D3-binding protein (Gc protein)
- Deglycosylated Gc protein cannot be converted into GcMAF, leading to immunosupression
- However: GcMAF from cancer patients has a demonstrated high macro- phage phagocytic effectiveness
Two Types of Nagalase
- Exo-type and endo-type
- Exo-type nagalase is secreted by: Cancer cells, virus-infected cells and normal cells
- Endo-type nagalase is secreted by: Cancer cells and virus-infected cells
- Specific to each disease
- Both endo-type and exo-type substrate are used to measure nagalase
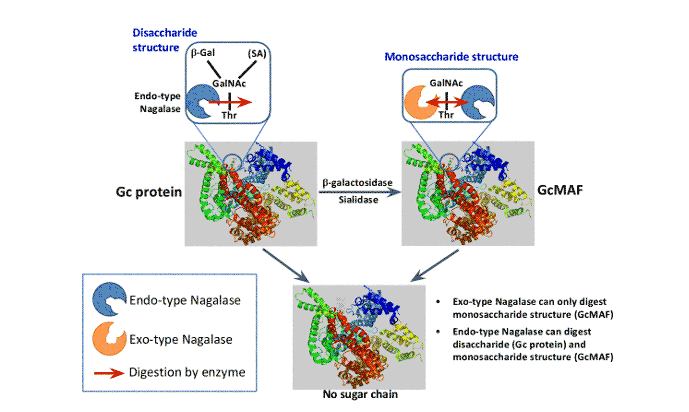
Role of Endo/exo-type Nagalase for the Digestion of the Sugar Chain of Gc Protein and GcMAF
How does first-generation GcMAF compare to and second-generation GcMAF?
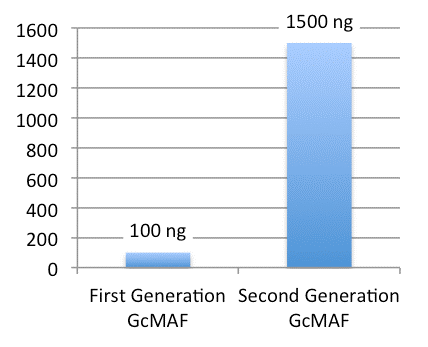
First-Generation GcMAF
- Developed by Dr Yamamoto in 1991
- Low concentration (100 ng/0.25 ml, 1 dose)
- Low stability at room temperature
- 25-(OH) Vitamin D3 Affinity Column
- Unstable in the absence of antioxidants such as albumin and uric acid
Second-Generation GcMAF
- Developed by the University of Tokushima and Saisei Mirai in 2010
- High concentration (1500 ng/0.5 ml, 1 dose)
- Significantly higher stability and macrophage activation
- New patented production process

Second-Generation GcMAF
What exactly is second-generation GcMAF?
High-Dose second-generation Gc-MAF is produced using by a new process, patent pending developed in Japan by Saisei Mirai in collaboration with Dr Hitoshi Hori and Dr Yoshihiro Uto at the University of Tokushima who have been studying GcMAF for over 20 years. Studies on GcMAF began at the University of Tokushima in 1992 after the two scientists were introduced to Dr Nobuto Yamamoto’s work resulting in a collaboration.
How does the new GcMAF differ from previous GcMAF versions?
Second-generation GcMAF is made using a new and improved second-generation method of Gc-MAF production which is 10-20 times more concentrated and more effective and stable than other GcMAF products currently available. Importantly, this much higher concentration GcMAF has been clinically demonstrated to be largely free of any side effects in the great majority of patients and is much more stable because it is resistant to oxidation.
First-Generation GcMAF vs Second-Generation GcMAF Concentration
How is GcMAF tested for effectiveness?
Our GcMAF is tested for macrophage phagocytic effectiveness using mouse macrophages and red blood cells from sheep at the University of Tokushima, Japan. The red blood cells are opsonized which marks them for ingestion and destruction by activated macrophages. Under a microscope, they can be seen as purple areas inside the clear cells. From this, the Phagocytosis (ingestion) Index (PI) can be calculated
See also Tests of second-generation GcMAF for further details.
How stable is second-generation GcMAF?
second-generation GcMAF is stable for a minimum of 2 weeks at room temperature. See our Stability of GcMAF in Serum (PDF) report produced by Tokushima University. We completed a longer stability experiment which found that second-generation GcMAF is stable for 4 weeks at room temperature without a loss in macrophage activation effectiveness so the GcMAF remains highly potent. We estimate from our experiments that our GcMAF remains highly potent without a loss in effectiveness for at least one month at room temperature. Refrigerated, there is no loss in effectiveness for over a year.
How long have you been producing second-generation GcMAF?
Saisei Mirai clinic has been producing our patented second-generation GcMAF since 2011 and physicians have treated over 1000 patients in Japanese clinics.
Where do you produce second-generation GcMAF?
We produce GcMAF in our own Saisei Mirai Cell Processing Center (CPC) in Osaka, Japan. Second-generation GcMAF is also available in Europe. Resurrection Clinics in the Netherlands
What other immunotherapies do you provide?
In addition to GcMAF, we produce NK cells (called Hyper T/NK Cell Therapy), lymphocytes and dendritic cells (DC). We are continuously researching and developing new immunotherapies for patients in collaboration with various universities in Japan.
Oral GcMAF
What is oral GcMAF?
Oral GcMAF is a form of GcMAF produced from bovine colostrum by Saisei Mirai and developed in collaboration with Tokushima University.
How does oral GcMAF differ from second-generation GcMAF?
oral GcMAF is produced in a similar way to second-generation GcMAF but uses bovine colostrum instead of serum. It is administered orally and sublingually. See GcMAF Therapy for more details below.
Who can take oral GcMAF?
Anyone can take oral GcMAF to stay healthy and fight off disease.
Is oral GcMAF a replacement for second-generation Gc-MAF?
For most serious illnesses, we recommend a combination of oral GcMAF and GcMAF injections. Because the site of administration differs, so too does the area of macrophage activation and the resulting effect.
Oral GcMAF made from bovine colostrum
What are the commonly observed clinical effects of oral GcMAF?
We have observed a number of common clinical effects from oral GcMAF such as:
- Improved sleep, more energy; reduced fatigue
- Improved digestion, reduced nocturnal urination
- Improved hair regrowth and reduced hair loss due to natural ageing
- Improved skin condition & smoothness
- Improved control or curing of infectious diseases such as virus, bacteria and other pathogens
- Reduced allergy symptoms, pollinosis and atopy
Is oral GcMAF tested for effectiveness?
Oral GcMAF is tested for macrophage phagocytic effectiveness using mouse macrophages and red blood cells from sheep at the University of Tokushima in Japan. See How is GcMAF tested for effectiveness?, Second-Generation GcMAF and Tests of Second-Generation GcMAF for further details.
How long does oral GcMAF remain effective?
Oral GcMAF is stable with high macrophage phagocytic effectiveness for at least a year. Long-term stability testing is currently being conducted. To maintain maximum long-term effectiveness, we recommend that oral MAF is refrigerated.
GcMAF Therapy
Which diseases can be treated with GcMAF therapy?
Gc-MAF and/or oral Colostrum MAF macrophage activation therapy is indicated in the treatment of any disease in which there is an immune dysfunction or where the immune system is compromised, such as:
| Cancer | Autoimmune diseases | Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | Herpes Simplex virus (HSV) | Cystitis |
| Hepatitis C virus (HCV) | Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Urinary tract infection (UTI) |
| (ASD) | Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) | Endometriosis |
| Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) | Lyme Disease (Lyme borreliosis) | IgA deficiency disorder |
| Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME) | Mycobacteria infections | Parkinson's Disease |
| Tuberculosis | Fibromyalgia | Human papillomavirus (HPV) |
| Lupus (Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE) | HIV AIDS | Dengue fever |
| Pneumonia infection | Warts caused by viral infection | Norovirus |
| Malaria | Influenza virus (flu) | Herpes simplex virus (HSV) |
| Q fever (Coxiella burnetii) | Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) | Chicken pox (varicella zoster virus) |
| Psoriasis | Respiratory tract infections | Ulcerative colitis, Crohn's Disease |
| Type 1 diabetes (T1DM), insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM) | Type 1.5 diabetes, Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA) |
What is the usual dose in GcMAF therapy?
Cancer
For second-generation GcMAF therapy, we recommend 0.5 ml High-Dose GcMAF (1500 ng/0.5 ml) 2-3 times a week for an integrative approach to treating cancer.
- More frequent dosing (daily or every other day) may be safely used with a more advanced stage of the disease, or initially in the course of treatment.
- GcMAF may also be administered by intravenous (IV) injection, 0.5-1.0 ml 2-3 times per week in 20 ml portions or more if deemed necessary, such as for advanced cases.
- We recommend IV GcMAF in addition to the usual weekly IM/SC injections. These can be administered on alternating days.
Other illnesses (such as Autism, CFS, ME, Lyme Disease)
We recommend 0.25 ml High-Dose GcMAF (1500 ng/0.5 ml) 2-3 times a week. Initial doses may start at 0.1 ml in the 1st week, 0.2 ml in the 2nd week and 0.25 ml or 0.3 ml in the 3rd week. A higher dose of 0.5 ml 2-3 times per week may be required depending on the initial response. See our Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) page for further details on Autism.
How is GcMAF administered?
GcMAF is administered by subcutaneous (SC) or intramuscular (IM) injection, 2-3 times per week (or as prescribed by the treating physician) using a size 26G x 1/2″ (0.45 x 13 mm) or a size 27G needle with a 2.5 ml or 1 ml syringe (single use, sterile, disposable). The larger 2.5 ml syringe is easier to use due to the shorter plunger stroke required during injection. Diabetes needles may also be sufficient for GcMAF administration although these needles are finer.
Treatment in our clinics has also been by intravenous (IV) and intratumoral (IT) injection although for most patients IM and SC injection is by far the most common means of administration. Good aseptic technique using pharmaceutical ethanol (ethyl alcohol) to swab the top of vials before inserting needles is required for vial use.
Various other methods of administration are possible:
Intravenous (IV) Injection
GcMAF may be administered by intravenous (IV) infusion (drip) or push IV. The usual dose is 0.5-1.0 ml 2-3 times per week in 20 ml or more saline. When given by push IV, 20 ml saline and GcMAF solution is administered in a 20 or 30 ml syringe for 3 minutes or longer.
Inhalation of GcMAF Using a Nebulizer
Another option of administration is using a Nebulizer to activate macrophages in the bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) of the lungs, for example, using a device such as the Omron NE-U22 Portable Nebuliser. This method of administra-tion is particularly well suited to pulmonary diseases where local administration can have greater effect.
 Omron NE-U22 Portable Nebulizer for administration in the lungs to activate macrophages in the Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT) of the lungs.
Omron NE-U22 Portable Nebulizer for administration in the lungs to activate macrophages in the Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT) of the lungs.
Oral administration Using Colostrum MAF in Enteric Capsules
Saisei Mirai Oral Colostrum MAF in enteric capsules provides another means of administration to Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT).
When taking a Colostrum MAF capsule that is enterically coated (hence not digested in the acid environment of the stomach) orally, the Colostrum MAF reaches the gut and activates macrophages in the Peyer’s Patches in the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). The gut-associated lymphoid tissue accounts for about 70 % of our body’s immune system. Oral administration is best on an empty stomach before food in the morning, before bedtime or about 30 minutes before meals to allow quicker passage of the capsule through the stomach to the gut.

Macrophages are abundant in the Peyer’s patches of the intestine
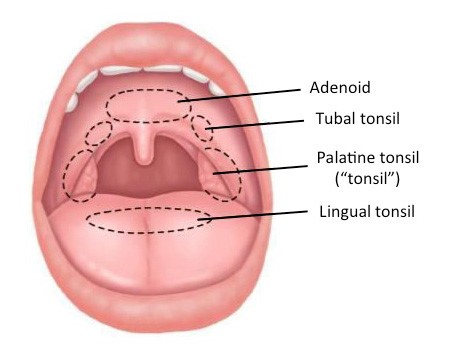
Sublingual administration of Colostrum MAF
Lymphoid tissue in the mouth and throat contains macrophages. When administering oral Colostrum MAF powder by opening the capsules and putting the powder in our mouth for 15-20 minutes or longer, these macrophages are activated. It is also possible that some GcMAF is absorbed sublingually through the blood vessels in the mouth, however, activation of macrophages in the lymphoid tissue of the throat is believed to be the most effective method. Lymphoid tissue is the part of the body’s immune system that is important for the immune response and helps protect from infection and foreign bodies. For example, people who suffer from Immunoglobulin A (IgA) and Immunoglobulin M (IgM) deficiency can benefit from this form of administration.
Lymphoid tissue of the mouth
How long should GcMAF therapy be continued?
One High-Dose GcMAF course usually consist of 48 doses for 6 months. Additional courses may be required depending on stage and type of disease and based on disease symptoms, pathology and progress of improvement. Treatment with GcMAF should be continued as long as necessary while disease is present. Long term maintenance doses of GcMAF may be required depending on the type of disease. Maintenance doses are usually administered once a week or every 2 weeks.
Generally speaking, macrophage activation is always necessary for the effective functioning of the immune system to stay healthy and disease-free. GcMAF therapy should be continued as long as the disease is present and for a period afterwards to reduce the chance of recurrence.
What tests should be carried out during GcMAF therapy?
We recommend checking tumor markers and regular MRI, PET and CT scans.
Monocyte Count: A patient’s monocyte count will generally rise in the early stages of GcMAF treatment in response to the GcMAF.
Increase in Monocyte Percentage with High-Dose GcMAF Therapy
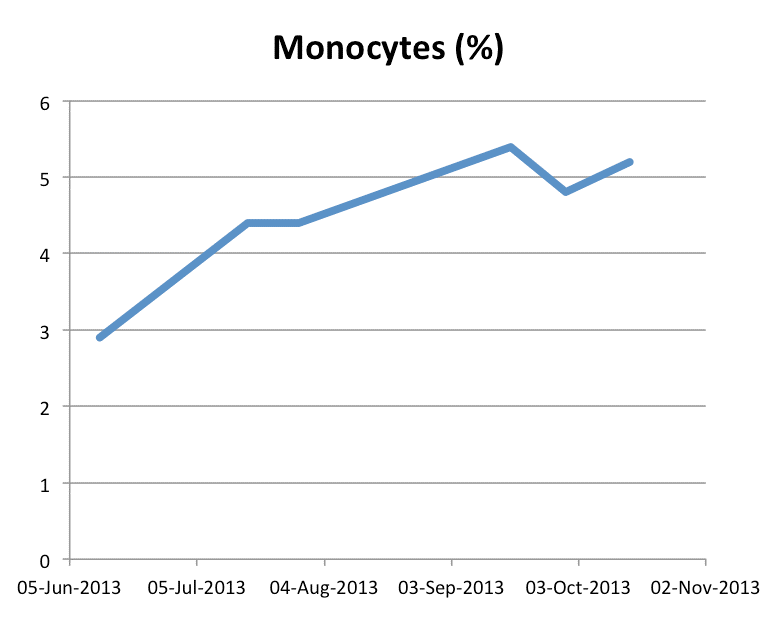
Increase in Monocyte Number with High-Dose GcMAF Therapy

Example of monocyte count of Stage 4 breast cancer patient taking 0.5 ml High-Dose GcMAF (1500 ng/0.5 ml) twice weekly by intra-muscular injection during cancer treatment
Are there any side effects with GcMAF?
Second-generation GcMAF has been clinically demonstrated to be largely free of any side effects in the great majority of patients. Only low-grade fever or eczema has been observed in only about 1 out of 100 patients using second-generation GcMAF but these were short-term effects that are significantly less than those that occur with most other immunotherapies. In a small number of patients, skin reactions occur at local injection sites which can be easily treated with a local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory patch.
Can GcMAF be used with other conventional therapies?
Generally, yes. GcMAF can be safely used with a wide variety of other standard treatments and drugs to improve their effect. This is referred to as multimodality integrative medicine. Some therapies for cancer such as chemotherapy will reduce immune effectiveness which has some impact on GcMAF, however, chemotherapy effectiveness can be increased in combination with GcMAF. Cancer-treating radiation has a less negative impact on the immune system and the cancer-killing effects helps macrophages to target tumors and destroy them.
A combination of anti-cancer drugs and radiation therapy (radiotherapy) is possible. For maximum effect and a greater GcMAF benefit, administration should be a few days apart from chemotherapy. Radiation therapy does not have significant effects on Gc-MAF, so both can be used together at any time. In our clinical experience, we have observed significant cancer-killing effects from GcMAF combined with palliative radiotherapy in patients exposed to major prior treatment with chemotherapy. See our Case Reports for more details on multimodality integrative treatment.
Are there any supplements I need to take with GcMAF?
GcMAF is usually combined with about 5,000 IU of vitamin D3 a day. Blood levels of vitamin D are often low with many illnesses such as cancer, HIV AIDS, etc. Normal vitamin D levels are required for GcMAF to work fully. Have your 25 hydroxy-vitamin D as well as calcium levels in the blood tested. If the calcium level in the blood is high, vitamin D3 may have to be reduced to achieve an optimal balance.
What should I avoid while using GcMAF?
Gc-MAF can be safely used with a wide variety of drugs and other treatments but minimal use of steroids is desirable because of their immune suppressing effect. They may, however, be used safely with GcMAF if necessary and prescribed by your physician.
Is nagalase testing necessary for GcMAF therapy?
Nagalase testing is not required for GcMAF therapy because macrophage activation is always necessary for the effective functioning of the immune system to destroy cancer cells, bacteria and viruses. GcMAF therapy should continue as long as the disease is present regardless of nagalase status.
Ordering and Shipping
How will I pay for GcMAF therapy?
Payment is by bank transfer to our account in the Netherlands. Please contact us to confirm your order and then make the transfer.
How long does it take for my parcel to arrive?
It usually takes 3-6 days to ship to all countries in the world. Some delays may occur for various reasons but this will not affect the stability of second-generation GcMAF. Please refer to our Stability of GcMAF report.
How much does shipping and handling cost?
Shipping and handling is 150 € worldwide. Prices include shipping and handling costs. Shipping can be calculated for other parcel delivery services such as FedEx, UPS or DHL.
How is GcMAF packaged for shipping?
The GcMAF is packaged in an insulated shipping box with ice packs to keep the temperature stable during shipment. The effectiveness of second-generation GcMAF does not decline during shipping at room temperature and even at temperatures as high as 40 °C (140 °F). Please see the GcMAF stability test report.













